Phishing Email Analysis: Ledger Impersonation Scam
Estimated read time: 4 min
Phishermen Prey on Trust
Phishing emails continue to grow in sophistication. I recently received a convincing email impersonating Ledger, a popular provider of cryptocurrency wallets. This case study dissects the indicators of compromise to help you spot more sophisticated phishing emails. This email requesting a recovery phrase verification landed in my inbox:
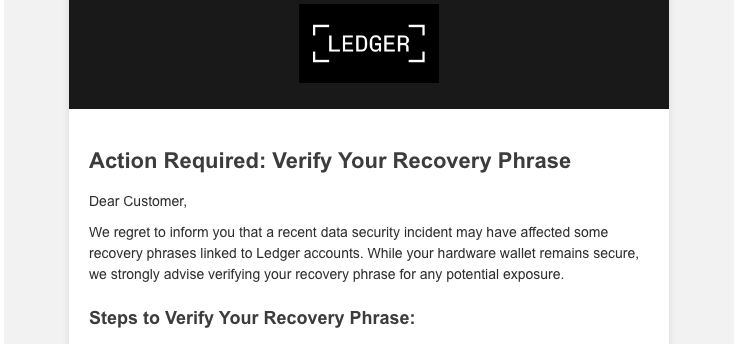
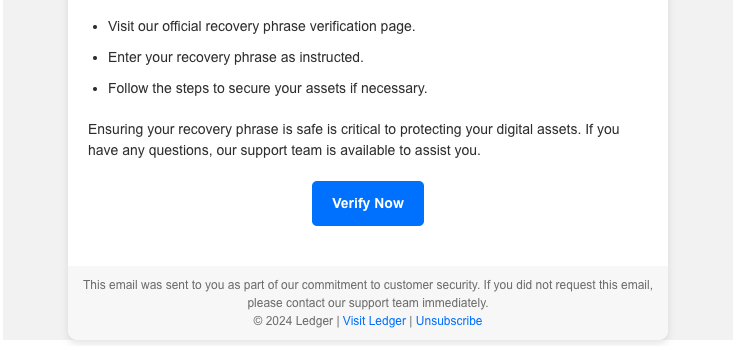 This screenshot doesn't give justice to the email's presentation in my inbox.
This screenshot doesn't give justice to the email's presentation in my inbox.
At first glance, it appears to be legitimate. Security experts and tech-aware professionals are typically immediately suspicious of unsolicited emails requesting verification of sensitive details, but not everyone shares that same skepticism.
Key components of trust
- well-formatted, branded, presented professionally
- native english without grammar and spelling errors
- sender set to "Ledger Notice" from
[email protected]instead of something more suspicious like[email protected] - subject line appears helpful: "Action Required: Ledger Data Breach – Check Your Recovery Phrase."
- security notice in footer includes legitimate links to Ledger's website
The messaging in this email is enough to convince most people that it's real. Although the email is well-crafted, there are several indicators of compromise that reveal its true nature. These look like glaring red flags to security professionals, but can be easily overlooked by the average person.
Indicators of compromise
Evaluating an email for compromise is often unnecessary because they usually give themselves away with poor formatting or broken english. Emails like this fake Ledger notice require deeper analysis to identify the threat. Here's a couple quick strategies to identify the more blatant indicators of compromise in this situation.
- Unsolicited verification request: corporations are not in the practice of requesting sensitive information via email. This is always a red flag.
- Check the sender's domain: the email was sent from
recover.com, not Ledger's official domain. - Hover over links: desktop browsers allow you to hover over links for a url preview. The link in this email points to an AWS S3 bucket, not Ledger's website. Exercise caution when doing this. Malware can be executed on hover, but well-designed email clients prevent scripts from running on hover. Do not attempt on mobile. Long-pressing a link provides similar functionality, but the risk of accidental execution is high.
- Review destination links in footer: the footer includes a security notice and links to Ledger's website, but doesn't include contact details for the security team.
Digging deeper
Inspecting the HTML content of the email helps unravel the deception:
The "Verify Now" link leads to an AWS S3 bucket, not Ledger's website. This is a common tactic used by phishers to mask the true destination of malicious links. Using a scanner like urlscan.io reveals that the true destination url:
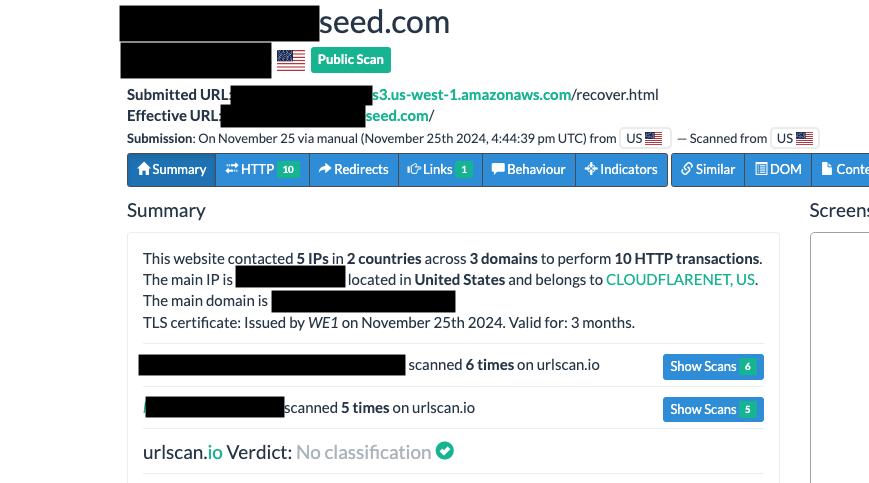 Details redacted to protect more curious readers.
Details redacted to protect more curious readers.
These results aren't alarming on their own, but the redirect does raise suspicion! Checking the destination url with VirusTotal reveals that the link has been flagged as malicious by several malware engines.
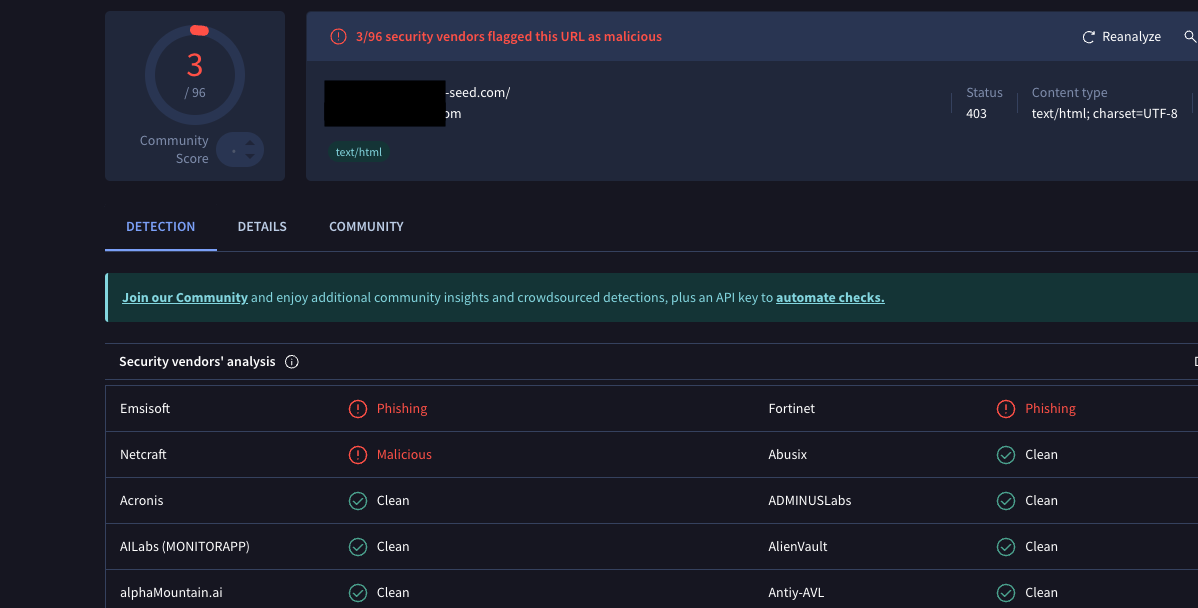 Details redacted to protect more curious readers.
Details redacted to protect more curious readers.
Impact of a successful attack
A successful phishing attack of this nature could result in complete loss of funds for victims. Be cautious of unsolicited emails requesting sensitive information. Always verify the sender's domain and verify destination url's to ensure they lead to legitimate destinations. If you receive an email like this, report it to the company being impersonated and delete it immediately.
